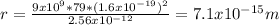Answer:
The radius of the gold nucleus is 7.1x10⁻¹⁵m
Step-by-step explanation:
The nearest distance is:
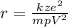 (eq. 1)
(eq. 1)
Where
z = atomic number of gold = 79
e = electron charge = 1.6x10⁻¹⁹C
k = electrostatic constant = 9x10⁹Nm²C²
energy of the particle = 32 MeV = 5.12x10⁻¹²J
At the potential energy is zero, all the energy will be kinetic energy:
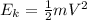
Where
m = 4 mp = mass of proton
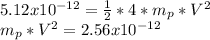
Replacing in equation 1