Answer:
Null hypothesis:
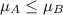
Alternative hypothesis:
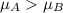
Since we dpn't know the population deviations for each group, for this case is better apply a t test to compare means, and the statistic is given by:
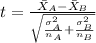 (1)
(1)
Now we need to find the degrees of freedom given by:
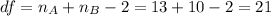
And now since we are conducting a right tailed test we are looking ofr a value who accumulates 0.05 of the are on the right tail fo the t distribution with df =21 and we got:

And for this case the rejection zone would be:
E. Reject H0 if t > 1.721
Explanation:
Data given and notation
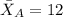 represent the mean for 1
represent the mean for 1
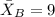 represent the mean for 2
represent the mean for 2
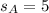 represent the sample standard deviation for 1
represent the sample standard deviation for 1
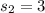 represent the sample standard deviation for 2
represent the sample standard deviation for 2
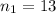 sample size for the group 1
sample size for the group 1
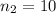 sample size for the group 2
sample size for the group 2
t would represent the statistic (variable of interest)
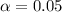 significance level provided
significance level provided
Develop the null and alternative hypotheses for this study
We need to conduct a hypothesis in order to check if the mean for group A is higher than the mean for B:
Null hypothesis:
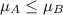
Alternative hypothesis:
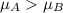
Since we dpn't know the population deviations for each group, for this case is better apply a t test to compare means, and the statistic is given by:
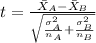 (1)
(1)
Now we need to find the degrees of freedom given by:
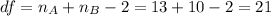
And now since we are conducting a right tailed test we are looking ofr a value who accumulates 0.05 of the are on the right tail fo the t distribution with df =21 and we got:

And for this case the rejection zone would be:
E. Reject H0 if t > 1.721