Answer:
a) Null hypothesis:
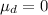
Alternative hypothesis:
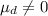
b)
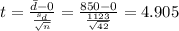
The next step is calculate the degrees of freedom given by:
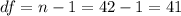
Now we can calculate the p value, since we have a left tailed test the p value is given by:
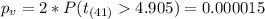
So the p value is lower than any significance level given, so then we can conclude that we can reject the null hypothesis that the difference between he two groups are equal.
Explanation:
Assuming the following questions:
We assume the following data:
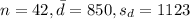
Previous concepts
A paired t-test is used to compare two population means where you have two samples in which observations in one sample can be paired with observations in the other sample. For example if we have Before-and-after observations (This problem) we can use it.
a. Formulate the null and alternative hypotheses to test for no difference between the population mean credit card charges for groceries and the population mean credit card charges for dining out.
The system of hypothesis for this case are:
Null hypothesis:
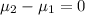
Alternative hypothesis:
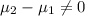
Or equivalently
Null hypothesis:
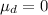
Alternative hypothesis:
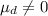
b. Use a .05 level of significance. Can you conclude that the population means differ? What is the p-value?
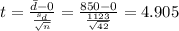
The next step is calculate the degrees of freedom given by:
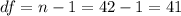
Now we can calculate the p value, since we have a left tailed test the p value is given by:
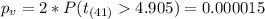
So the p value is lower than any significance level given, so then we can conclude that we can reject the null hypothesis that the difference between he two groups are equal.