Answer:
The expected freezing point of a 1.75 m solution of ethylene glycol is -3.26°C.
Step-by-step explanation:
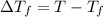
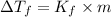
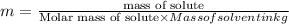
where,
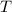 = Freezing point of solvent
= Freezing point of solvent
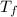 = Freezing point of solution
= Freezing point of solution
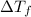 =depression in freezing point
=depression in freezing point
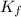 = freezing point constant
= freezing point constant
m = molality
we have :
Mass of ethylene glycol = 59.0 g
Molar mass of ethylene glycol = 62.1 g/mol
Mass of solvent i.e. water = 543 g = 0.543 kg ( 1 g = 0.001 kg)
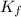 =1.86°C/m ,
=1.86°C/m ,
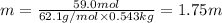
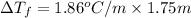
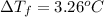
Freezing point of pure water = T = 0°C
Freezing point of solution =
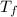
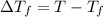
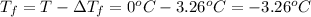
The expected freezing point of a 1.75 m solution of ethylene glycol is -3.26°C.