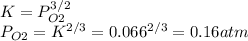Answer:
a) ΔGrxn = 6.7 kJ/mol
b) K = 0.066
c) PO2 = 0.16 atm
Step-by-step explanation:
a) The reaction is:
M₂O₃ = 2M + 3/2O₂
The expression for Gibbs energy is:
ΔGrxn = ∑Gproducts - ∑Greactants
Where
M₂O₃ = -6.7 kJ/mol
M = 0
O₂ = 0
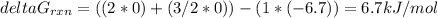
b) To calculate the constant we have the following expression:
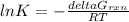
Where
ΔGrxn = 6.7 kJ/mol = 6700 J/mol
T = 298 K
R = 8.314 J/mol K
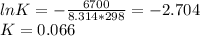
c) The equilibrium pressure of O₂ over M is: