Answer:
Maximum value:
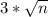
Minimum value:

Explanation:
Let
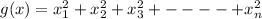 , the restriction function.The Lagrange Multiplier problem states that an extreme (x1, ..., xn) of f with the constraint g(x) = 9 has to follow the following rule:
, the restriction function.The Lagrange Multiplier problem states that an extreme (x1, ..., xn) of f with the constraint g(x) = 9 has to follow the following rule:
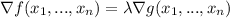
for a constant
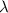 .
.
Note that the partial derivate of f respect to any variable is 1, and the partial derivate of g respect xi is 2xi, this means that
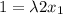
Thus,
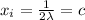
Where c is a constant that doesnt depend on i. In other words, there exists c such that (x1, x2, ..., xn) = (c,c, ..., c). Now, since g(x1, ..., xn) = 9, we have that n * c² = 9, or
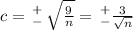
When c is positive, f reaches a maximum, which is
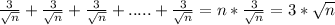
On the other hand, when c is negative, f reaches a minimum,
