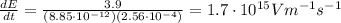Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
The electric field between the plates of a parallel-plate capacitor is given by
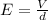 (1)
(1)
where
V is the potential difference across the capacitor
d is the separation between the plates
The potential difference can be written as
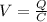
where
Q is the charge stored on the plates of the capacitor
C is the capacitance
So eq(1) becomes
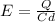 (2)
(2)
Also, the capacitance of a parallel-plate capacitor is
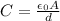
where
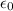 is the vacuum permittivity
is the vacuum permittivity
A is the area of the plates
Substituting into (2) we get
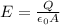 (3)
(3)
Here we want to find the rate of change of the electric field inside the capacitor, so
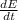
If we calculate the derivative of expression (3), we get
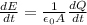
However,
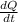 corresponds to the definition of current,
corresponds to the definition of current,
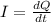
So we have
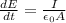
In this problem we have
I = 3.9 A is the current
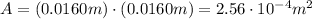 is the area of the plates
is the area of the plates
Substituting,