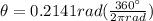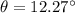To solve this problem we will apply the concepts related to the double slit experiment. Here we test a relationship between the sine of the deviation angle and the distance between slit versus wavelength and the bright fringe order. Mathematically it can be described as,
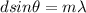
Here,
d = Distance between slits
m = Any integer which represent the order number or the number of repetition of the spectrum
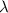 = Wavelength
= Wavelength
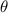 = Angular deviation
= Angular deviation
Replacing with our values we have,
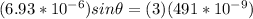
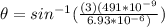
Part A)
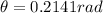
PART B)