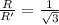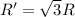Answer:
New radius of the charge particle when potential is increased by 3times of initial value
Step-by-step explanation:
As we know that charge particle is accelerated due to potential difference V then we have
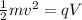
now the speed of the charge particle is given as
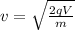
now in constant magnetic field which is perpendicular to the motion of charge we have
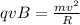
now we have
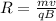
now we have
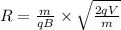 [/tex]
[/tex]
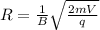
now if we changed the potential to three times of initial value then we have
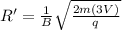
so we have