Answer:
The correct option is;
3. Dims in, Brightens out
Step-by-step explanation:
Inserting the iron rod into the current carrying solenoid causes the inductance and hence impedance to increase. Increasing impedance increases the circuit total resistance to current flow, thereby reducing the amount of electric current, which causes the light bulb to dim as the iron rod enters the solenoid.
The reverse happens as the iron rod is rapidly removed.
The inductive reactance is given by;
Inductive reactance,
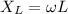 = 2·π·f·L
= 2·π·f·L
Where;
L = Inductance (Henries)
ω = Angular velocity in radians
f = Frequency
current, I is given by
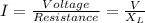
Therefore
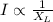
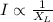
Iron rod entering the solenoid increases inductance, decreases the current and the bulb is dimmer.