The angle of the wedge is 30°.
Answer:
5.88 ft/s
Step-by-step explanation:
a) The block will slide down due to it's weight.
initial velocity u= 0
final velocity, v
acceleration, a = g sin 30° = 32 ft/s²× sin 30° = 16 ft/s²
Sliding displacement, s = 3ft
Use third equation of motion:
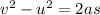
substitute the values and solve for v
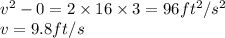
b) Use conservation of momentum:
Initial momentum of the system = 0
final momentum = (15) ( 9.8)+ (25)(v')
v' = 5.88 ft/s