Answer:
(d) equal to one-fourth the acceleration at the surface of the asteroid.
Step-by-step explanation:
From Newton's gravitational law, force between two objects (planet) is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of their distance apart.
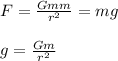
Case 1: when the ball rises to a height equal to the asteroid's radius
height, h = r
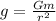
Case 2: when the ball rises to a height equal to the asteroid's radius and falls straight down toward the surface of the asteroid.
At top of its path, total height is 2r.
h = 2r
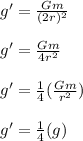
Therefore, the acceleration of the ball at the top of its path is equal to one-fourth the acceleration at the surface of the asteroid.
Option "d"