Answer: The pH after 0.02 mol of
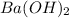 are added to 0.72 L of the solution is 9.5.
are added to 0.72 L of the solution is 9.5.
Step-by-step explanation:
The chemical equation for the dissociation of base represented by B in water is depicted as follows.
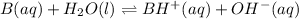
According to Henderson-Hasselbach equation,
pH =
![pK_(a) + log ([B])/([BH^(+)])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/slqb2q3zt72j703v4kauq9dwopuq4l5m32.png)
9.31 =
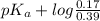
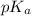 = 9.31 + 0.361
= 9.31 + 0.361
= 9.671
Initial moles of B is as follows.
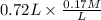
= 0.1224 mol B
Now, the initial concentration of
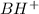 is as follows.
is as follows.
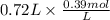
= 0.281 mol
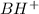
We will calculate the equilibrium moles after the addition of 0.02 moles
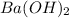 which is 0.04 moles
which is 0.04 moles
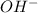 as follows.
as follows.
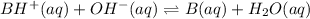
Initial: 0.281 0.04 0.1224
Change: -0.04 -0.04 +0.04
Equilbm: 0.241 0 0.1624
Hence,
pH =
![pK_(a) + log ([B])/([BH^(+)])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/slqb2q3zt72j703v4kauq9dwopuq4l5m32.png)
=
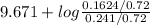
=
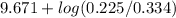
= 9.671 - 0.171
= 9.5
Thus, we can conclude that the pH after 0.02 mol of
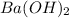 are added to 0.72 L of the solution is 9.5.
are added to 0.72 L of the solution is 9.5.