Answer: For the given reaction an increase in the forward reaction rate due to increase in the number of effective collisions.
Step-by-step explanation:
According to the rate law, rate of a reaction depends on the concentration of its reactants. So, more is the number of reactants then more will be the number of collisions taking place.
As a result, more will be the amount of product formed. For example, in the reaction
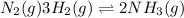 an increase in
an increase in
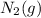 means an increase in the number of reactants.
means an increase in the number of reactants.
Hence, more is the number of collisions taking place leading to more amount of formation of products.
Thus, we can conclude that for the given reaction an increase in the forward reaction rate due to increase in the number of effective collisions.