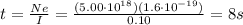Answer:
8 seconds
Step-by-step explanation:
The current in a wire is defined as
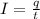
where
q is the charge passing through a given point of the wire in a time t
In a metal wire, the current is generally carried by electrons. So, the charge passing through a certain point of the wire can be written as
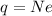
where
N is the number of electrons
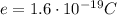 is the fundamental charge (the charge of one electron)
is the fundamental charge (the charge of one electron)
So the formula becomes
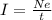
In this metal wire we have
I = 0.10 A is the current in the wire
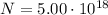 is the number of electrons
is the number of electrons
Solving for the time, we find: