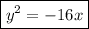Answer:
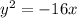
Explanation:
Equation of the Parabola
The standard form of the parabola with the axis of symmetry parallel to the y-axis, vertex at (h.k) and directrix y=k-p is
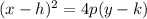
If the parabola has its axis of symmetry parallel to the x-axis, vertex at (h.k) and directrix x=h-p is
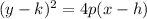
The focus of this form of the parabola is located at (h+p,k)
The parabola described in the question belongs to the second form since the directrix is at x=4. We also know that the focus is at (-4,0). We can find the values of h and p by equating
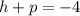
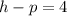
Adding up both equations
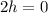
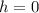
then
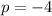
The vertex is (h,k)=(0,0)
We can now write the equation of the parabola as
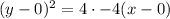
Simplifying