Answer:
The probability that a person has HIV\AIDS given that the person was tested positive for HOV|AIDS is 0.1060.
Explanation:
Let a set be events that have occurred be denoted as:
S = {A₁, A₂, A₃,..., Aₙ}
The Bayes' theorem states that the conditional probability of an event, say Aₙ given that another event, say X has already occurred is given by:
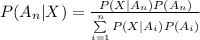
The screening test for HIV/AIDS designed by a pharmaceutical company is being analysed.
Denote the events as follows:
A = a person has HIV/AIDS
X = the test turns out as positive
The information provided is:
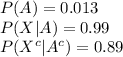
The probability that the test result is positive given that the person does not have HIV\AIDS is:
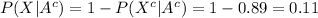
Compute the value of P (A|X) using the Bayes' theorem as follows:
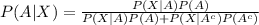
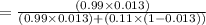
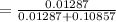
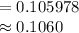
Thus, the probability that a person has HIV\AIDS given that the person was tested positive for HOV|AIDS is 0.1060.