Answer:
a = 2.75*10^{15}m/s^2
Step-by-step explanation:
The acceleration of the electron is generated by the Lorenz's force, due to the magnetic field produced by the wire. Hence, we have
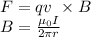
I=18.9 A
r=2.35cm=0.0235m
mu=4pi*10^{-7}
v=(0.325)(3*10^{8}m/s)=9.75*10^{7}m/s
q=1.6*10^{-19} C
By replacing these values in the expression for B we have
B=1.6*10^{-4} T
The direction of the magnetic field is perpendicular to the direction of the motion of the electron. Thus
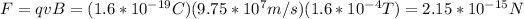
And by replacing this factor in F=ma we have
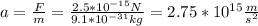
where we have used the mass of the electron.
hope this helps!!