Answer:
The 95% confidence intervals are (530.4 ,569.6) of sample means under the null hypothesis
Explanation:
The mean score on a particular standardized test is μ=500
and also standard deviation of(σ) = 100.
random sample n =100
mean of the sample from data Χ⁻=550
95% of confidence intervals
The mean score on a particular standardized test is 'μ"
and also standard deviation of( σ) the population
size of the sample 'n'
mean of the ( Χ⁻ ) from the sample
level of significance z_{0.05} = 1.96 ( from z- tabulated value area at 0.95)
In this data we will use 95% of confidence intervals of the mean of the sample are given by
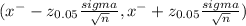
we will substitute given data
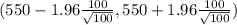
on simplification , we get
(530.4 ,569.6)
The 95% confidence intervals are (530.4 ,569.6) of sample means under the null hypothesis