Answer: The
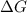 for the given reaction at 298 K is -64.11 kJ/mol
for the given reaction at 298 K is -64.11 kJ/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
For the given chemical equation:
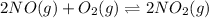
The equation used to Gibbs free energy of the reaction follows:
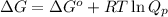
where,
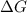 = free energy of the reaction
= free energy of the reaction
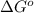 = Standard Gibbs free energy = -69.0 kJ/mol = -69000 J/mol (Conversion factor: 1 kJ = 1000 J)
= Standard Gibbs free energy = -69.0 kJ/mol = -69000 J/mol (Conversion factor: 1 kJ = 1000 J)
R = Gas constant = 8.314 J/K mol
T = Temperature = 298 K
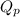 = Ratio of partial pressure of products and reactants =
= Ratio of partial pressure of products and reactants =
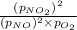
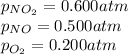
Putting values in above equation, we get:
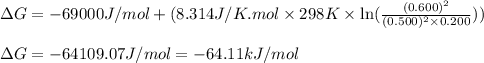
Hence, the
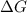 for the given reaction at 298 K is -64.11 kJ/mol
for the given reaction at 298 K is -64.11 kJ/mol