Answer: The activation energy for the reaction is 40.143 kJ/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate activation energy of the reaction, we use Arrhenius equation for two different temperatures, which is:
![\ln((K_(317K))/(K_(278K)))=(E_a)/(R)[(1)/(T_1)-(1)/(T_2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/1752glbowht7a586b5llhbzu14nz3iob25.png)
where,
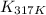 = equilibrium constant at 317 K =
= equilibrium constant at 317 K =
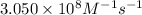
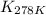 = equilibrium constant at 278 K =
= equilibrium constant at 278 K =
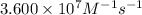
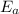 = Activation energy = ?
= Activation energy = ?
R = Gas constant = 8.314 J/mol K
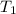 = initial temperature = 278 K
= initial temperature = 278 K
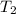 = final temperature = 317 K
= final temperature = 317 K
Putting values in above equation, we get:
![\ln((3.050* 10^8)/(3.600* 10^(7)))=(E_a)/(8.314J/mol.K)[(1)/(278)-(1)/(317)]\\\\E_a=40143.3J/mol=40.143kJ/mol](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/ogzdwhqgs3kihe4p6whtjv63scvf39p6p6.png)
Hence, the activation energy for the reaction is 40.143 kJ/mol