Answer: The value of equilibrium constant for Equation 2 is
![K'=\sqrt[3]{(1)/(K)}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/ni2peay1t4534m03wec7rwhki8vofbzyhr.png)
Step-by-step explanation:
The chemical equation whose equilibrium constant is given follows:
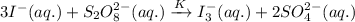 ......(1)
......(1)
The chemical equation whose equilibrium constant is to be calculated follows:
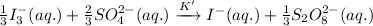 .........(2)
.........(2)
As, the Equation 2 is the result of the reverse of one-third of Equation 1. So, the equilibrium constant for the Equation 2 will be the cube root of inverse of equilibrium constant of Equation 1.
The value of equilibrium constant for Equation 2 is:
![K'=\sqrt[3]{(1)/(K)}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/ni2peay1t4534m03wec7rwhki8vofbzyhr.png)
Hence, the value of equilibrium constant for Equation 2 is
![K'=\sqrt[3]{(1)/(K)}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/ni2peay1t4534m03wec7rwhki8vofbzyhr.png)