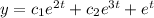Answer:
Therefore the complete primitive is
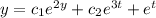
Therefore the general solution is
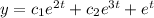
Explanation:
Given Differential equation is
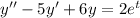
Method of variation of parameters:
Let
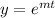 be a trial solution.
be a trial solution.
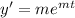
and
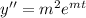
Then the auxiliary equation is
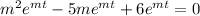
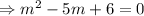
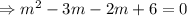
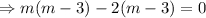
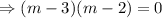
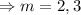
∴The complementary function is
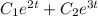
To find P.I
First we show that
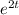 and
and
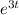 are linearly independent solution.
are linearly independent solution.
Let
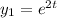 and
and
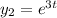
The Wronskian of
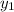 and
and
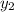 is
is
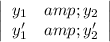
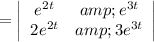
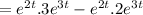
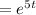 ≠ 0
≠ 0
∴
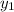 and
and
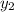 are linearly independent.
are linearly independent.
Let the particular solution is
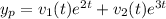
Then,
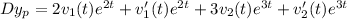
Choose
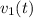 and
and
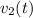 such that
such that
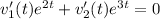 .......(1)
.......(1)
So that
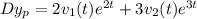
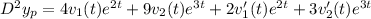
Now
![4v_1(t)e^(2t)+9v_2(t)e^(3t)+ 2v'_1(t)e^(2t)+3v'_2(t)e^(3t)-5[2v_1(t)e^(2t)+3v_2(t)e^(3t)] +6[v_1e^(2t)+v_2e^(3t)]=2e^t](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/bc38ftrihndbpnt2q5ru236l0yszvxywqc.png)
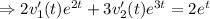 .......(2)
.......(2)
Solving (1) and (2) we get
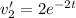 and
and
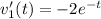
Hence
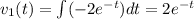
and
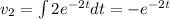
Therefore
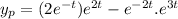
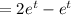
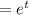
Therefore the complete primitive is
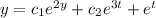
Undermined coefficients:
∴The complementary function is
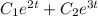
The particular solution is
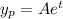
Then,
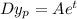 and
and
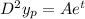
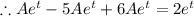
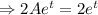
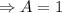
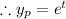
Therefore the general solution is