Answer:
The final pressure of the mixture = 444.4 k pa
Step-by-step explanation:
Given data for oxygen
Mass of oxygen = 1 kg
Temperature = 15 °c= 298 K
Pressure P = 300 K pa
Volume of the oxygen
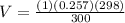
V = 0.25
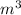
Mole number of oxygen is
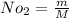
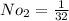
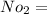 0.03125 k mol
0.03125 k mol
Given data for nitrogen
Volume of Nitrogen = 2
Temperature = 50 °c= 323 K
Pressure = 500 K pa
Mass of nitrogen
m =
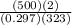
m = 10.43 kg
Now mole number of nitrogen
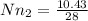
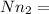 0.372 k mol
0.372 k mol
Thus the mole number of mixture is the sum of mole no. of oxygen & mole no. of nitrogen.
N =
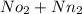
N = 0.03125 + 0.372
N = 0.4035 k mol
Therefore the final pressure of the mixture is given by the ideal gas equation
P V = N R T ------- (1)
Where P = final pressure of the mixture
V = 0.25 + 2 = 2.25
N = total no. of moles in final mixture = 0.4035 K mol
T = final temperature of the mixture = 298 K
Put all the values in equation 1 , we get
P × 2.25 = 0.4035 × 8.314 × 298
P = 444.4 K pa
Therefore the final pressure of the mixture = 444.4 k pa