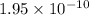Answer: The equilibrium constant for this reaction is
Step-by-step explanation:
Equilibrium constant is the ratio of the concentration of products to the concentration of reactants each term raised to its stochiometric coefficients.
The given balanced equilibrium reaction is,
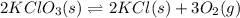
At eqm. conc. (2.00) M ( 0.00250 ) M (0.0500) M
The expression for equilibrium constant for this reaction will be,
![K_c=([KCl]^2* [O_2]^3)/([KClO_3]^2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/a5m73985p5z84tzsz39eju7hj9wlhv87qa.png)
Now put all the given values in this expression, we get :
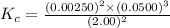
By solving we get :
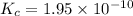
Thus the equilibrium constant for this reaction is