Answer:
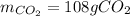
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, the undergoing chemical reaction is:
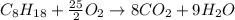
In such a way, the limiting reagent is determined by the comparison between the available moles of octane and the moles of octane consumed by 123 g of oxygen as shown below:
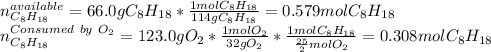
In such a way, since there are less grams consumed by the oxygen, octane is in excess whereas oxygen is the limiting reagent, therefore, the minimum amount of produced carbon dioxide by the reaction is:
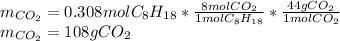
In this case, three significant figures should be used based on the initial data.
Best regards.