Answer: 1). Weak acids are usually one of the following: 1. hydrofluoric acid,
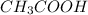 .
.
2). Acids in which the proton is not bonded to an oxygen atom or a halogen (ex. HCN ).
3). Oxo-acids where the number of oxygen atoms equals or only exceeds by 1 the number of ionizable protons (ex.
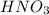 ) or
) or
4). Carboxylic acids (ex.
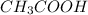 ).
).
Step-by-step explanation:
Weak acids are the species which partially dissociate into ions when added to water. For example, acetic acid (
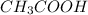 ) is a weak acid.
) is a weak acid.
Acids in which the proton is not bonded to an oxygen atom or a halogen is HCN.
Oxo-acids are the acids which contain oxygen atom. For example,
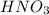 ,
,
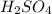 , R-COOh etc are all oxo-acids.
, R-COOh etc are all oxo-acids.
In oxo-acids, the number of oxygen atoms equals or only exceeds by 1 the number of ionizable protons.
Thus, we can conclude that:
1). Weak acids are usually one of the following: 1. hydrofluoric acid,
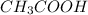 .
.
2). Acids in which the proton is not bonded to an oxygen atom or a halogen (ex. HCN ).
3). Oxo-acids where the number of oxygen atoms equals or only exceeds by 1 the number of ionizable protons (ex.
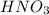 ) or 4. Carboxylic acids (ex.
) or 4. Carboxylic acids (ex.
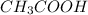 ).
).