Answer:
To=20.44 °C
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that
Velocity , v= 30 m/s
Temperature , T= 20°C
We know that specific heat capacity for air ,Cp=1.005 kJ/kg.K
By using energy conservation ,the stagnation temperature is given as
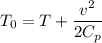
Now by putting the values in the above equation we get
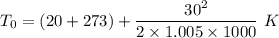
To= 293.44 K
To= 293.44 - 273 °C
To=20.44 °C
Therefore the stagnation temperature will be 20.44 °C.