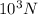Answer:
F = 5.256 x
Step-by-step explanation:
From the work energy theorem we know that:
The net work done on a particle equals the change in the particles kinetic energy:
W = F.d, ΔK =
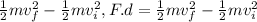
where:
W = work done by the force
F = Force
d = Distance travelled
m = Mass of the car
vf, vi = final and initial velocity of the car
kf, ki = final and initial kinetic energy of the car
Given the parameters;
m = 830kg
vi = 1.9 m/s
vf = 0 km/h
d = 0.285 m
Inserting the information we have:
F.d =
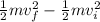
F =
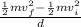
F =
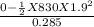
F = 5.256 x