Answer: The maximum amount of water that could be produced by the chemical reaction is 20.16 grams
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the number of moles, we use the equation:
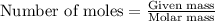 .....(1)
.....(1)
Given mass of butane = 13 g
Molar mass of butane = 58.12 g/mol
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
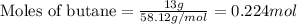
Given mass of oxygen gas = 70.9 g
Molar mass of oxygen gas = 32 g/mol
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
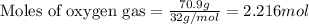
The chemical equation for the reaction of butane and oxygen gas follows:
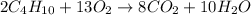
By Stoichiometry of the reaction:
2 moles of butane reacts with 13 moles of oxygen gas
So, 0.224 moles of butane will react with =
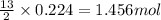 of oxygen gas
of oxygen gas
As, given amount of oxygen gas is more than the required amount. So, it is considered as an excess reagent.
Thus, butane is considered as a limiting reagent because it limits the formation of product.
By Stoichiometry of the reaction:
2 moles of butane produces 10 moles of water
So, 0.224 moles of butane will produce =
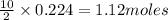 of water
of water
Now, calculating the mass of water from equation 1, we get:
Molar mass of water = 18 g/mol
Moles of water = 1.12 moles
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
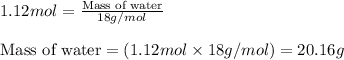
Hence, the maximum amount of water that could be produced by the chemical reaction is 20.16 grams