Answer:
![\sqrt[3]{0.95} \approx 0.983\\\\\\\sqrt[3]{1.1} \approx 1.033](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/pjnxrqn5oawv7zh3vgy4dzf4tgsx2jhbya.png)
Explanation:
The function is:
![g(x) =\sqrt[3]{1+x}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/3xd5yiug01z3og0zc7kvjjukowepd7xnks.png)
We can find a linear aproximation around a point with a Taylor's series:
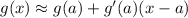
The value of g(a) is
![g(a)=g(0)=\sqrt[3]{1+0}=1](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/s1ly3m6vdz0q1v8md5o0qaier76cszomd4.png)
We have to calculate the firste derivative of g(x):
![g'(x)=(d)/(dx)[(1+x)^ {1/3}]=(1/3)(1+x)^(-2/3)=(1)/(3(1+x)^(2/3))](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/qrlccgp262jglsgw9b4b1iydbbd0ym5kl4.png)
Then, we calculate g'(a)
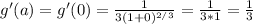
The linear approximation is:
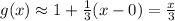
Calculate
![\sqrt[3]{0.95}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/m7dl6reg4lm4l4jy8fbmpj17il69c7rxrw.png)
We can use the linear approximation to calculate this, with x=-0.05.
![0.95=1+x\rightarrow x=-0.05\\\\\sqrt[3]{0.95} \approx 1+((-0.05))/(3) =1-0.017=0.983](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/3o1y991ltd9yljgh54zwtt8h65h8cykuea.png)
Calculate
![\sqrt[3]{1.1}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/fz2xozhug3d89rtvu2x9sc2dmkdx5o9i1e.png)
We can use the linear approximation to calculate this, with x=0.1.
![1.1=1+x\rightarrow x=0.1\\\\\sqrt[3]{1.1} \approx 1+((0.1))/(3) =1+0.033=1.033](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/g66i5531ng2zqwqiqoiqc17h5qrmslh75d.png)