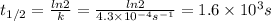Answer:
1.6 × 10³ s
Step-by-step explanation:
Let's consider the following generic reaction.
A → B
The rate law is:
![rate=k * [A]^(m)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/phoplwz269mx26eugs4ni9hka91vbcv48b.png)
where,
rate is the reaction rate
k is the rate constant
[A] is the molar concentration of the reactant A
m is the reaction order
When m = 1, we have a first-order reaction. We can calculate the half-life for this reaction using the following expression.