Answer:
Velocity will be equal to 7.31 m/sec
Step-by-step explanation:
We have given mass of the student m = 61 kg
Height of the water slide h = 12.3 m
Acceleration due to gravity
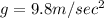
Potential energy is equal to
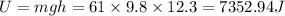
Work done due to friction = -5800 J
So energy remained = 7352.94-5800 = 1552.94 J
This energy will be equal to kinetic energy
So
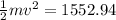
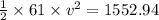
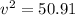
v = 7.13 m/sec