Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
charge, q = 10 C
time, t = 2 micro second
Current, i = q / t
i = 10 / (2 x 10^-6) = 5 x 10^6 A
(a)
distance, d = 1 m
the formula for the magnetic field is given by
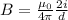
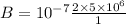
B = 1 Tesla
Now the distance is d' = 1 km = 1000 m
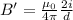
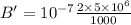
B' = 0.001 Tesla
(b) The magnetic field of earth is Bo = 3 x 10^-5 tesla
B / Bo = 3.3 x 10^4
B'/Bo = 33.3