Answer: The final concentration of sulfide anion in the solution is 0.297 M
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the number of moles for given molarity, we use the equation:
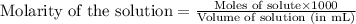 .....(1)
.....(1)
Molarity of barium sulfide solution = 0.173 M
Volume of solution = 23.5 mL
Putting values in equation 1, we get:

1 mole of barium sulfide (BaS) produces 1 mole of barium ions
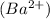 and 1 mole of sulfide ions
and 1 mole of sulfide ions
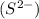
Moles of sulfide ions = (1 × 0.0041) = 0.0041 moles
Molarity of sodium sulfide solution = 0.402 M
Volume of solution = 27.7 mL
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
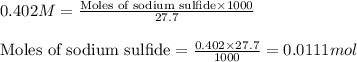
1 mole of sodium sulfide
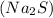 produces 2 moles of sodium ions
produces 2 moles of sodium ions
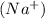 and 1 mole of sulfide ions
and 1 mole of sulfide ions
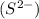
Moles of sulfide ions = (1 × 0.0111) = 0.0111 moles
Now, calculating the concentration of sulfide anion in the solution by using equation 1, we get:
Total moles of sulfide ions = [0.0041 + 0.0111] = 0.0152 moles
Total volume of the solution = [23.5 + 27.7] = 51.2 mL
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
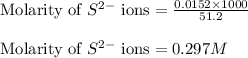
Hence, the final concentration of sulfide anion in the solution is 0.297 M