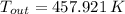Answer:
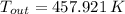
Step-by-step explanation:
Before determining the exit temperature of air, it is required to find the specific enthalpy at outlet by using the First Law of Thermodynamics:
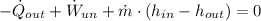
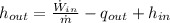
An ideal gas observes the following mathematical model:
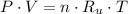
Where:
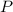 - Absolute pressure, in kilopascals.
- Absolute pressure, in kilopascals.
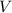 - Volume, in cubic meters.
- Volume, in cubic meters.
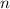 - Quantity of moles, in kilomole.
- Quantity of moles, in kilomole.
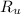 - Ideal gas universal constant, in
- Ideal gas universal constant, in
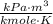 .
.
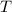 - Absolute temperature, in kelvin.
- Absolute temperature, in kelvin.
The previous equation is re-arranged in order to calculate specific volume at inlet:
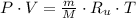
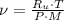
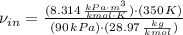
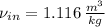
The mass flow is:
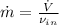
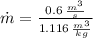
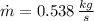
The specific enthalpy in ideal gases depends on temperature exclusively. Then:
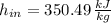
The specific enthalpy at outlet is:
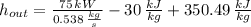
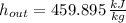
The exit temperature of air is: