Answer: The actual yield of the carbon dioxide is 47.48 grams
Step-by-step explanation:
For the given balanced equation:
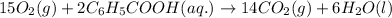
To calculate the mass for given number of moles, we use the equation:
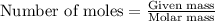
Theoretical moles of carbon dioxide = 1.30 moles
Molar mass of carbon dioxide = 44 g/mol
Putting values in above equation, we get:
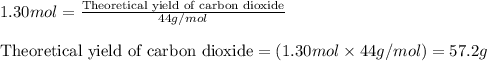
To calculate the theoretical yield of carbon dioxide, we use the equation:
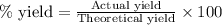
Theoretical yield of carbon dioxide = 57.2 g
Percentage yield of carbon dioxide = 83.0 %
Putting values in above equation, we get:
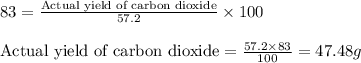
Hence, the actual yield of the carbon dioxide is 47.48 grams