Answer:
Optimal order quantity is 17,664 units
Step-by-step explanation:
Optimal order quantity is the quantity at which business incur minimum cost. This is the level of order where the holding cost equals to the ordering cost of the business.
As per given Data
Demand = 500 units per week = 500 units x 52 weeks = 26,000 units
Ordering Cost = $60
As the limit of the is 2,300 or below the product cost is $0.05 and the inventory cost is 20% of the product cost.
Inventory cost = $0.05 x 20% = $0.01
Optimal order quantity =
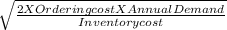
Optimal order quantity =
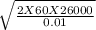
Optimal order quantity = 17,664 units