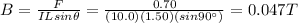Answer:
0.047 T
Step-by-step explanation:
When a current-carrying wire is placed in a region with a magnetic field, the wire experiences a force, given by the equation
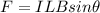
where
I is the current in the wire
L is the length of the wire
B is the strength of the magnetic field
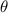 is the angle between the direction of B and I
is the angle between the direction of B and I
In this problem:
L = 1.50 m is the length of the wire
I = 10.0 A is the current in the wire
F = 0.70 N is the force exerted on the wire
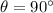 since the current is at right angle with the field
since the current is at right angle with the field
Solving for B, we find the strength of the magnetic field: