The pressure acting on an area of 20 m² with force 50 N is 2.5 Nm² and the pressure acting on an area of 0.5 m² with force 50 N is 100 Nm².
The force acting on area of 3 m² with pressure 10 Pa is 30 N.
Step-by-step explanation:
Pressure acting on any surface is the amount of force experienced by that surface in a given area. So it is the ratio of force to area of the object under consideration.
As here the force is said to be 50 N and the area is said to be 20 m², the pressure will be
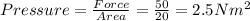
So, pressure is inversely proportional to the area and directly proportional to the force acting on the surface. As it can be seen that on decreasing the area to 0.5 m², there will be increase in the pressure as shown below,
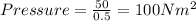
Thus, the pressure increased to 100 Nm² from 2.5 Nm² on decreasing the area from 20 m² to 0.5 m².
Similarly, if 10 Pa pressure is acting on an area of 3 m², then the force acting on this region will be the product of pressure with the area.
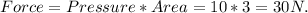
Thus, the pressure acting on an area of 20 m² with force 50 N is 2.5 Nm² and the pressure acting on an area of 0.5 m² with force 50 N is 100 Nm².
The force acting on area of 3 m² with pressure 10 Pa is 30 N.