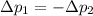Answer:
Their change in momentum is the same in magnitude and opposite in direction
Step-by-step explanation:
The momentum of an object is defined as:
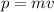
where
m is the mass of the object
v is the velocity of the object
Therefore, the change in momentum of an object is
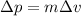
where
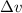 is the change in velocity.
is the change in velocity.
During a collision, the force experienced by an object is equal to the rate of change of momentum:
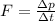
where
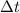 is the duration of the collision.
is the duration of the collision.
According to Newton's third law of motion, the force exerted by vehicle 1 on vehicle 2 during the collision is equal (and opposite) to the force exerted by vehicle 2 on vehicle 1, so
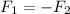
Which means
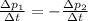
And since the duration of the collision is the same for the two vehicles, this becomes