Answer: The specific heat of metal is 0.507 J/g°C
Step-by-step explanation:
When metal is dipped in water, the amount of heat released by metal will be equal to the amount of heat absorbed by water.
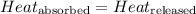
The equation used to calculate heat released or absorbed follows:
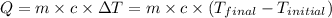
![m_1* c_1* (T_(final)-T_1)=-[m_2* c_2* (T_(final)-T_2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/8mq914tycmkoswztk5p5my04anxw73dmzg.png) ......(1)
......(1)
where,
q = heat absorbed or released
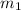 = mass of metal = 24.87 g
= mass of metal = 24.87 g
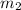 = mass of water = 76.12 g
= mass of water = 76.12 g
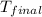 = final temperature = 28.2°C
= final temperature = 28.2°C
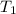 = initial temperature of metal = 104.0°C
= initial temperature of metal = 104.0°C
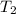 = initial temperature of water = 25.2°C
= initial temperature of water = 25.2°C
 = specific heat of metal = ?
= specific heat of metal = ?
 = specific heat of water = 4.186 J/g°C
= specific heat of water = 4.186 J/g°C
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
![24.87* c_1* (28.2-104)=-[76.12* 4.186* (28.2-25.2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/oaww03t0ruva96pwyhh8yvo3g9i8vnfrjy.png)
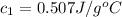
Hence, the specific heat of metal is 0.507 J/g°C