Answer:
Critical value is t = 1.9901
Explanation:
We are given the results of the sampling :
In-House Credit Card National Credit Card Sample Size : 32 50
Mean Monthly Purchases : $45.67 $39.87
Standard Deviation : $10.90 $12.47
Also, the managers wished to test whether there is a statistical difference in the mean monthly purchases by customers using the two types of credit cards, using a significance level α of 0.05.
Firstly, we will specify our null and alternate hypothesis;
Let
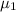 = Mean Monthly Purchases of In-House Credit Card
= Mean Monthly Purchases of In-House Credit Card
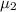 = Mean Monthly purchases of National Credit Card
= Mean Monthly purchases of National Credit Card
So, Null Hypothesis,
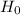 :
:
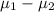 = 0 {means that there is no difference in the mean monthly purchases by customers using the two types of credit cards}
= 0 {means that there is no difference in the mean monthly purchases by customers using the two types of credit cards}
Alternate Hypothesis,
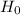 :
:
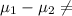 0 {means that there is statistical difference in the mean monthly purchases by customers using the two types of credit cards}
0 {means that there is statistical difference in the mean monthly purchases by customers using the two types of credit cards}
The test statistics that will be used here is Two-sample t-test statistics;
T.S. =
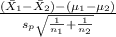 ~
~
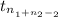
where,
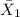 = Sample mean Purchases of In-House Credit Card = $45.67
= Sample mean Purchases of In-House Credit Card = $45.67
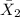 = Sample mean Purchases of National Credit Card = $39.87
= Sample mean Purchases of National Credit Card = $39.87
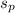 = pooled variance
= pooled variance
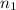 = In-house credit card sample = 32
= In-house credit card sample = 32
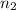 = National credit card sample = 50
= National credit card sample = 50
So, degree of freedom of t-value here is (32 + 50 - 2) = 80
Now, at 0.05 significance level, t table gives critical value of t = 1.9901 at 80 degree of freedom.
Therefore, the critical value assuming the population standard deviations are not known but that the populations are normally distributed with equal variances is t = 1.9901.