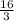Answer:
Explanation:
Given that:
The vector is the straight line, so to form the algebraic description of this vector we need to find out the slope of it:
Slope:
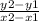 =
=
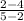 =
=
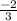
We have the standard form of the linear is:
y = mx +b
In this situation, y =
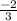 x + b (1)
x + b (1)
Because the line go through the point: (2, 4) so we substitute them into the equation (1): 4 =
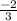 (2) + b <=> b =
(2) + b <=> b =
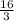
So the algebraic description of this vector is: y =
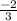 x +
x +