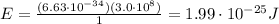Answer:
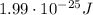
Step-by-step explanation:
Electromagnetic waves are oscillations of the electric and the magnetic field in a plane perpendicular to the direction of motion the wave.
All electromagnetic waves travel in a vacuum always at the same speed, the speed of light:
The energy of an electromagnetic wave is given by the equation:
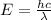
where:
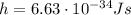 is the Planck constant
is the Planck constant
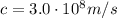 is the speed of light
is the speed of light
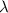 is the wavelength of the wave
is the wavelength of the wave
In this problem, we have a wave with wavelength of
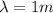
So, its energy is: