Answer:
Option B. -4819 kJ
Step-by-step explanation:
Equation of reaction:
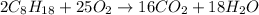 Δ
Δ
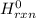 = -11018 kJ
= -11018 kJ
Mass of octane, m = 100.0 g
Molar mass of octane, MM = 114.33 g/mol
Number of mole, n = Mass/ Molar mass
Number of mole of octane, n = m/MM
n = 100/114.33
n = 0.8746 mols
From the chemical equation above
2 mols of octane produced -11018 kJ of heat
1 mol of octane produces (-11018/2) kJ of heat = -5509 kJ oh heat
Therefore, o.875 mols of octane will produce (-5509 * 0.8746) kJ oh heat = -4819 kJ of heat.