Answer:
Equilibrium constant for the reaction at 25⁰C = 1.81 x 10⁻⁶
Step-by-step explanation:
Reaction for the Haber's process
N₂(g) + 3 H₂(g) ⇌ 2 NH₃(g)
Free energy change of reaction
ΔGr° = ∑products free energy - ∑reactants free energy
= 2 x (- 16.4) - 0
= - 32.8 KJ / mole
Equilibrium constant for this reaction at 25⁰C
ΔGr° = - 2.303 RT log K
⇒ log K =
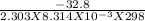
⇒ K = Anti log( -5.74) = 1.81 x 10⁻⁶