Answer: The
![[H_(2)O]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/on8zfqjyy5igdz40qay2mfl9pp5sbribcw.png) at equilibrium is 0.561 M.
at equilibrium is 0.561 M.
Step-by-step explanation:
The given data is as follows.
Volume of flask = 0.32 L,
No. of moles of
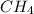 = 0.041 mol,
= 0.041 mol,
No, of moles of CO = 0.26 mol, No. of moles of
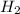 = 0.091 mol
= 0.091 mol
Equilibrium constant, K = 0.26
Balanced chemical equation for this reaction is as follows.
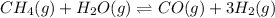
Hence,
K =
![([CO][H_(2)]^(3))/([CH_(4)][H_(2)O])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/z5vh4i3ma8k0zi1214g2jdnru0zdhnbbno.png) ...... (1)
...... (1)
First, we will calculate the molarity or concentration of given species as follows.
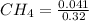 = 0.128 M,
= 0.128 M,
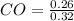 = 0.8125 M,
= 0.8125 M,
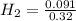 = 0.284 M
= 0.284 M
Therefore, using expression (1) we will calculate the
![[H_(2)O]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/on8zfqjyy5igdz40qay2mfl9pp5sbribcw.png) as follows.
as follows.
K =
![([CO][H_(2)]^(3))/([CH_(4)][H_(2)O])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/z5vh4i3ma8k0zi1214g2jdnru0zdhnbbno.png)
or,
![[H_(2)O] = ([CO][H_(2)]^(3))/([CH_(4)] * K)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/mq69cwilv280u9hk1rhjittmecat5qvv6x.png)
=
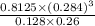
=
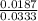
= 0.561 M
Thus, we can conclude that the
![[H_(2)O]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/on8zfqjyy5igdz40qay2mfl9pp5sbribcw.png) at equilibrium is 0.561 M.
at equilibrium is 0.561 M.