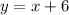Explanation:
A line can be repsented by slope-intercept form:
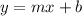
where
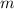 is the slope of the line and
is the slope of the line and
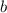 is the y-intercept.
is the y-intercept.
The slope of the line is represented by the change in the
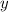 values on the line divided by the change in the
values on the line divided by the change in the
 values on the line, or, simply put,
values on the line, or, simply put,
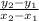
for any two points
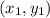 and
and
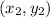 that are on the line.
that are on the line.
Taking any two points on the given line, we can see that the slope of the above graph is
 , so we can plug this in for
, so we can plug this in for
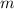 :
:
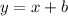
This eliminates options C and D.
Now, the y-intercept is the point at which the line crosses the y-axis, or, simply put, what the value of the line is at
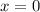 .
.
Looking at the line, it crosses the y-axis at
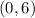 , meaning we can plug in
, meaning we can plug in
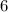 for
for
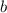 in our equation and get our answer:
in our equation and get our answer: