Answer:
A) Series
Step-by-step explanation:
The elements of an electric circuit can be connected in two different configurations:
- Series: two resistors are connected in series when they are connected along the same branch, so that the current flowing through them is the same. In this case, the equivalent resistance of the circuit is given by
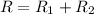
So, it is given by the sum of the individual resistances of the elements. In this case, the voltage drop acrosss each element is different.
This configuration is more simple to arrange, however it has a drawback: if one of the element is disconnected from the circuit (or it's broken), the whole circuit stops working.
- Parallel: two resistors are connected in parallel when thet are connected in different branches having the same potential difference across them. However, the current through them is different. In this case, the equivalent resistance is given by
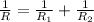
This configuration is more difficult to arrange, however if one of the element is disconnected from the circuit (or it's broken), the whole circuit keeps working.
In this figure, we see that the two light bulbs are connected along the same branch: therefore, they are connected in series.